Salivary Gland Cancer

This is a short video on the most common neoplasms (tumors and cancers) of the salivary glands.
I created this presentation with Google Slides.
Image were created or taken from Wikimedia Commons
I created this video with the YouTube Video Editor.
ADDITIONAL TAGS:
Neoplasms of the salivary glands
Pleomorphic adenoma
Warthin's tumor
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma
Adenoid cystic carcinoma
By Ed Uthman, MD - http://web2.airmail.net/uthman/specim..., Public Domain, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index...
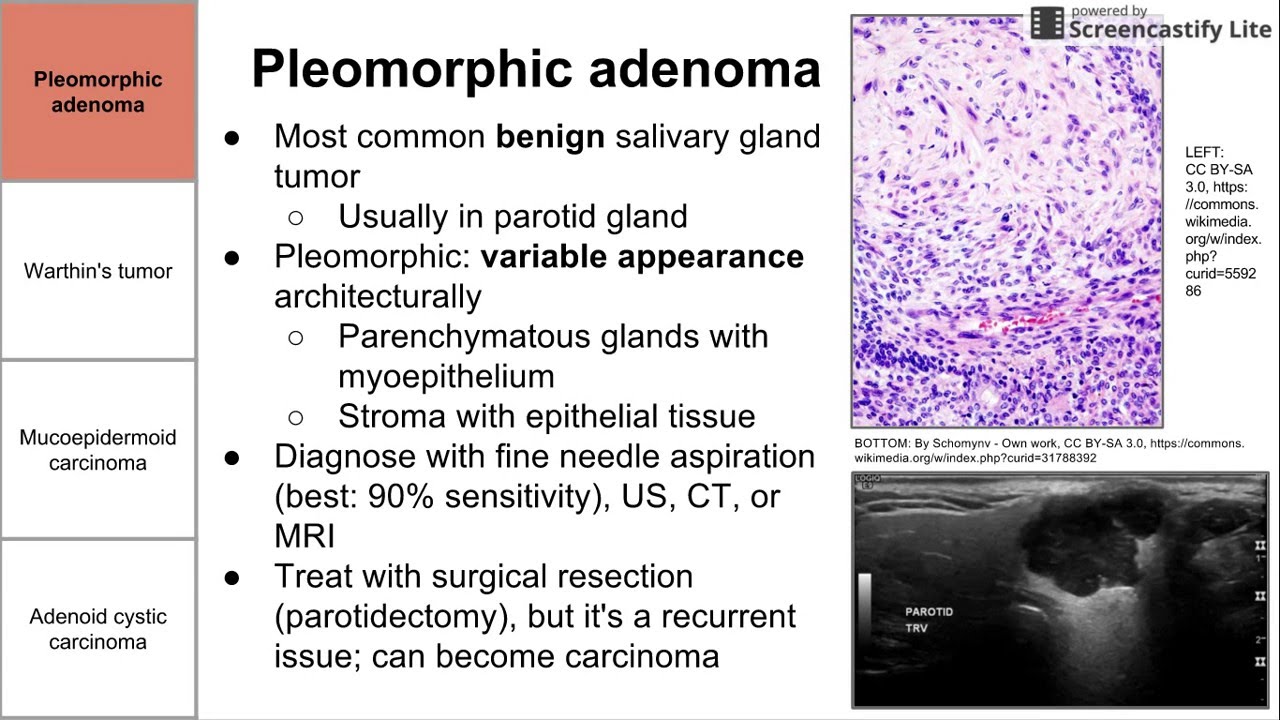
Pleomorphic adenoma
Most common benign salivary gland tumor
Usually in parotid gland
Pleomorphic: variable appearance architecturally
Parenchymatous glands with myoepithelium
Stroma with epithelial tissue
Diagnose with fine needle aspiration (best: 90% sensitivity), US, CT, or MRI
Treat with surgical resection (parotidectomy), but it's a recurrent issue; can become carcinoma
Pleomorphic adenoma
Warthin's tumor
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma
Adenoid cystic carcinoma
BOTTOM: By Schomynv - Own work, CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index...
LEFT:
CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index...
Warthin’s tumor
AKA papillary cystadenoma lymphomatosum
Second most common benign salivary gland tumor
Usually in parotid
Histo: germinal centers, cystic spaces, many lymphocytes, condensed chromatin (pyknotic) nuclei
Associated with smoking, older people
Tumor is slow growing, often painless
Pleomorphic adenoma
Warthin's tumor
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma
Adenoid cystic carcinoma
CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index...
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma
Most common malignant salivary gland tumor
Usually starts in parotid, can also be found outside of salivary gland
Histo: contains mucinous cells and squamous cells
Tumor is slow growing, often painless
Associated with CMV
Pleomorphic adenoma
Warthin's tumor
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma
Adenoid cystic carcinoma
By No machine-readable author provided. KGH assumed (based on copyright claims). - No machine-readable source provided. Own work assumed (based on copyright claims)., CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index...
By Nephron - Own work, CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index...
Adenoid cystic
carcinoma
Second most common malignant salivary gland tumor
Common tumor of the submandibular gland
Can also involve other tissues
Slow growing
Can have distant metastases: eye, lung, brain, sinuses, trachea, breast
Treatment is surgical resection, radiation
Pleomorphic adenoma
Warthin's tumor
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma
Adenoid cystic carcinoma
TOP:
By Jto410 - In my clinical work as a diagnostic radiologist, CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index...
BOTTOM:
By Nephron - Own work, CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index...


Eric Moore, M.D., a head and neck surgeon at Mayo Clinic, and Heidi, a Mayo Clinic patient, discuss the different types of parotid tumors.
Get Parotid Tumor Care Now. Call to obtain an appointment at Mayo Clinic, Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery 1-507-923-2443. See here to learn more about Parotid Tumors https://mayocl.in/3cu5iCE

Salivary gland cancer is a rare disease in which cancer cells form in the tissues of the salivary glands. But what are the early symptoms of salivary gland cancer? Our otolaryngologist Hakan Cıncık, MD talked about salivary gland cancer in detail and answered some of the most asked questions about the disease.
#salivaryglands #cancer #otolaryngologists
----------------------------------
At Istanbul Medical Assistance, we are committed to ensuring distance and language are not obstacles to receiving first-class care and helping you find the appropriate department and specialists. We are here to meet your unique healthcare needs in a convenient, affordable, and comfortable way for you. Istanbul Medical Assistance provides a single point of access to services and coordination for all referrals. Our team of highly specialized healthcare professionals helps you access these services and ensure your utmost comfort when you are in Istanbul.
----------------------------------
To know more
Website: https://istanbulmedassist.com/
Email: ipc@istanbulmedassist.com
Phone: +90 530 884 47 22
----------------------------------
Don’t forget to share, comment & or follow us to get more updates.


Joseph Zenga, MD, head and neck surgical oncologist, explains that the survival rate for salivary gland cancer depends on the type and stage of cancer, but the majority of salivary gland cancers can be treated successfully. Dr. Zenga is a member of the Froedtert & the Medical College of Wisconsin Head and Neck Cancer Program in Milwaukee, Wis.
https://www.froedtert.com/head....-neck-cancers/saliva


Salivary gland Neoplasm can be Benign or Malignant.
Majority of cases are c.
Malignant cancers are rare.
Malignant salivary gland tumors usually present after the 6th decade of life, whereas benign lesions present in the 4-5th decade of life.
The salivary glands make saliva and release it into the mouth.
There are 3 pairs of major salivary glands:
Parotid glands: These are the largest salivary glands and are found in front of and just below each ear. Most major salivary gland tumors begin in this gland.
Sublingual glands: These glands are found under the tongue in the floor of the mouth.
Submandibular glands: These glands are found below the jawbone.
here are also hundreds of small (minor) salivary glands lining parts of the mouth, nose, and larynx that can be seen only with a microscope. Most small salivary gland tumors begin in the palate (roof of the mouth).
Signs and Symptoms.
Some cases Salivary gland cancer can be asymptomatic.
In other cases:
A lump (usually painless) in the area of the ear, cheek, jaw, lip, or inside the mouth.
Fluid draining from the ear.
Trouble swallowing or opening the mouth widely.
Numbness or weakness in the face.
Pain in the face that does not go away.
Causes:
No single cause is known for Salivary gland Cancer, but Radiation exposure, head and neck radiation therapy, has been linked to parotid gland carcinomas, 15 years after the event.
Cigarette smoking and alcohol directly, are not associated with salivary gland tumor.
Salivary tumor among kids are very rare.
Most of cases occurs sixth decade of life.
Overall 5-year survival rate of salivary cancer is 70 % but highly dependent on stage and type of cancer.
Diagnosis.
Most common diagnostic tests are: Common tests are: MRI (magnetic resonance imaging): and CT scan (CAT scan). Endoscopy and Phisical examination.
Most patients with early-stage lesions that are resectable generally tend to undergo surgery as their initial therapeutic approach, whereas those with advanced or unresectable cancers tend to be treated with radiotherapy alone or chemoradiotherapy.
By BruceBlaus. When using this image in external sources it can be cited as:Blausen.com staff (2014). "Medical gallery of Blausen Medical 2014". WikiJournal of Medicine 1 (2). DOI:10.15347/wjm/2014.010. ISSN 2002-4436. - Own work, CC BY 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/....w/index.php?curid=29
By Jto410 - In my clinical work as a radiologist, CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/....w/index.php?curid=28


What are the symptoms of a salivary gland tumor? Dr. Ryan Osborne, Director of Head & Neck Surgery and Salivary Gland Disorders, at the Osborne Head & Neck Institute, specializes in the non-surgical removal of salivary gland stones causing swelling and infection of the major salivary glands. In this series of videos, Dr. Osborne answers frequently asked questions about salivary gland stones.
For in depth information, or to schedule your virtual consultation with Dr. Osborne, please visit: https://www.parotid.net/
View more FAQ videos about salivary gland stones here: https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLD7nLk0Vkgv
Watch surgical procedures, including salivary gland surgery, on our docu-series called OHNI Case Files: https://www.youtube.com/playli....st?list=PLD7nLk0Vkgv


Mark Rolfing was diagnosed with stage IV salivary gland cancer in August 2015. As a television golf analyst for NBC and the Golf Channel, Mark reflects on the multidisciplinary care that he received at MD Anderson, where teams of specialists care for patients from cancer diagnosis to treatment and beyond. To learn more about Mark’s journey, visit: https://www.mdanderson.org/pub....lications/cancerwise
Request an appointment at MD Anderson by calling 1-877-632-6789 or online: my.mdanderson.org/requestappointment.


Since his cancer diagnosis, parotid salivary gland cancer survivor Mohamed Sarani has changed his outlook on life, as well as his diet and that of his family. He no longer dwells on little things, tries to appreciate each day and wants his kids to learn to maintain a healthy lifestyle.
Read more cancer survivor stories: http://www2.mdanderson.org/cancerwise/
Request an appointment at MD Anderson: https://www4.mdanderson.org/co....ntact/selfreferral/i #endcancer



