Flow Cytometry - 4 | CD Markers| T cell Acute lymphoblastic leukemia & NK cells -- 10 MINUTES !!
#FLOW CYTOMETRY#CD MARKERS#T CELL ACUTE LYMPHOBLASTIC LEUKEMIA#T LYMPHOMA#HEMATOPOIESIS
the first video on flow cytometry:- https://youtu.be/e407J69aMvc
the second video on flow cytometry:- https://youtu.be/X5SHdFAymQw
the third video on flow cytometry:-https://youtu.be/aJw8zdoaZSI
the fourth video on flow cytometry:-https://youtu.be/GJbtkMo1Alw
flow cytometry,flowcytometry,cd markers,must know cd markers,pathogenesis flow cytometry,t cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia,t cell lymphoma,t cell maturation,t cells,t cells and b cells,hematopoiesis,flow cytometry tutorial,flow cytometry data analysis,flow cytometry animation,flow cytometry basics,acute lymphoblastic leukemia,acute lymphoblastic leukemia symptoms,t cell activation,acute leukemia,acute lymphocytic leukemia,Flow cytometry cd markers
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=e407J69aMvc
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=X5SHdFAymQw
This video is the fourth part of the basics of flow cytometry which covers hematopoiesis and CD Markers. Hematopoiesis and CD markers form the backbone of Flow Cytometry. CD markers is a very high yielding topic . Please do not enter exam hall without being sure that you know CD markers very well. After understanding the principles of a flow cytometry machine, we next move to the uses of flow cytometry in various hematological disorders. We will first understand normal hematopoiesis in the bone marrow. We will also understand about CD markers that form the basis of flow cytometry are used to label and identify different types of cells. Hematopoiesis is the process of creating new blood cells in the body. Each type of cell in blood has its own unique signature, whether it is a blast, lymphocyte, monocyte, neutrophil, or RBC. This signature is defined by CD markers. No matter how many times we read about CD markers and hematopoiesis, we tend to forget it. So, in this video, we will learn to apply CD markers in a practical way so that we can remember them
If we know how normal hematopoietic cells behave in flow cytometry plots, then only we can identify abnormal patterns in different types of leukemias.
Chapters
00:00 Introduction
00:19 Why to know T cell development?
01:10 Hematogones
01:44 T cell development - BMA
02:53 T cell development - Thymus
05:04 T cell development - Peripheral Tissues
05:29 T CD markers table
07:21 flow cytometry previous videos summary
08:20 NK cell development
Learning about CD markers is the key to understanding and interpretation of flow cytometry.
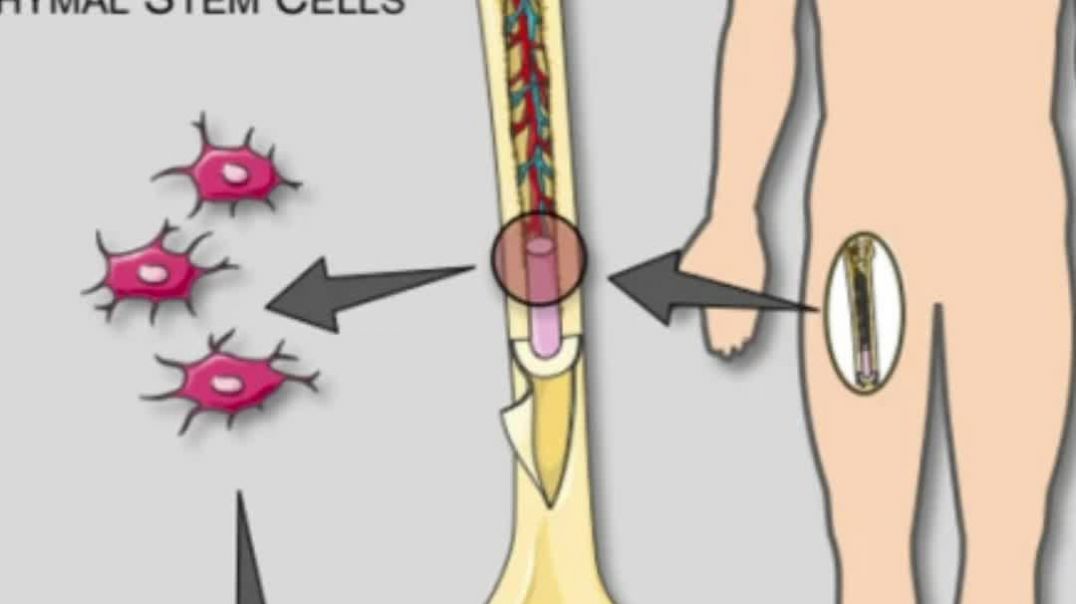
Hematopoiesis is the process of creating new blood cells in the body. All blood cells start off as hematopoietic stem cells and then specialize (differentiate) into myeloid cells (erythrocytes, megakaryocytes, monocytes, neutrophils, basophils, or eosinophils) or lymphoid cells (T-lymphocytes and B-lymphocytes).
#flowcytometry#hematopoiesis#flowcytometryanimation#erythropoesis#flowcytometrybasics #flowcytometrytechnique #flowcytometryprinicple #flowcytometrylightscattering #forwardscattering #sidescattering #flowcytometryaiims#flow cytometry
Many a times in flow cytometry we get a sample from a lymph node or a peripheral blood to be tested for presence of lymphoma or leukemia. However lymph node might be having reactive t cell proliferation due to infection , or peripheral blood lymphocytosis may again be reactive . So how do we differentiate ?
Knowing the cd markers present on t cell precursors and mature t cells, help us to interpret flow cytometry plots and separate a benign proliferation from a malignant one.
T-cell development begins in the bone marrow to form progenitor T-cells that undergo maturation and acquisition of function in the thymus and later in the peripheral lymphoid tissues such as blood, spleen, skin and mucosa.
Further differentiation occurs in the thymic cortex, through several stages.
Pro-t cells through the blood stream reach the subcapsular region of thymic cortex, and mature into Pre-T-cells. Pre-T cells are characterized by expression of TdT, CD7, CD2 and CD5.
CD 3 and CD7 are pan T cell markers i.e. they are present at all stages of a T lymphocyte. So, even Pre-T cells express CD3 but it is cytoplasmic. CD34 may be present in the first two stages and is never expressed beyond Pre-T. CD 2 is expressed Pre-T stage onwards. They are initially negative for both CD4 and CD8 (double negative [DN] T-cells).
Pre- T cells move from the subcapsular region to the cortex where they mature into cortical thymocytes.In the thymic cortex, DN T-cells loose CD34 and start to differentiate into double positive (DP) T-cells that is CD4+ and CD8+, through several stages.CD1a is expressed only on cortical T lymphocytes.




















SORT BY-
Top Comments
-
Latest comments