Laparoscopic oophorectomy (removal of the ovaries)
A short video demonstrating laparoscopic removal of the ovaries performed at the John Radcliffe Hospital Oxford.
http://www.oxfordgynaecology.com/
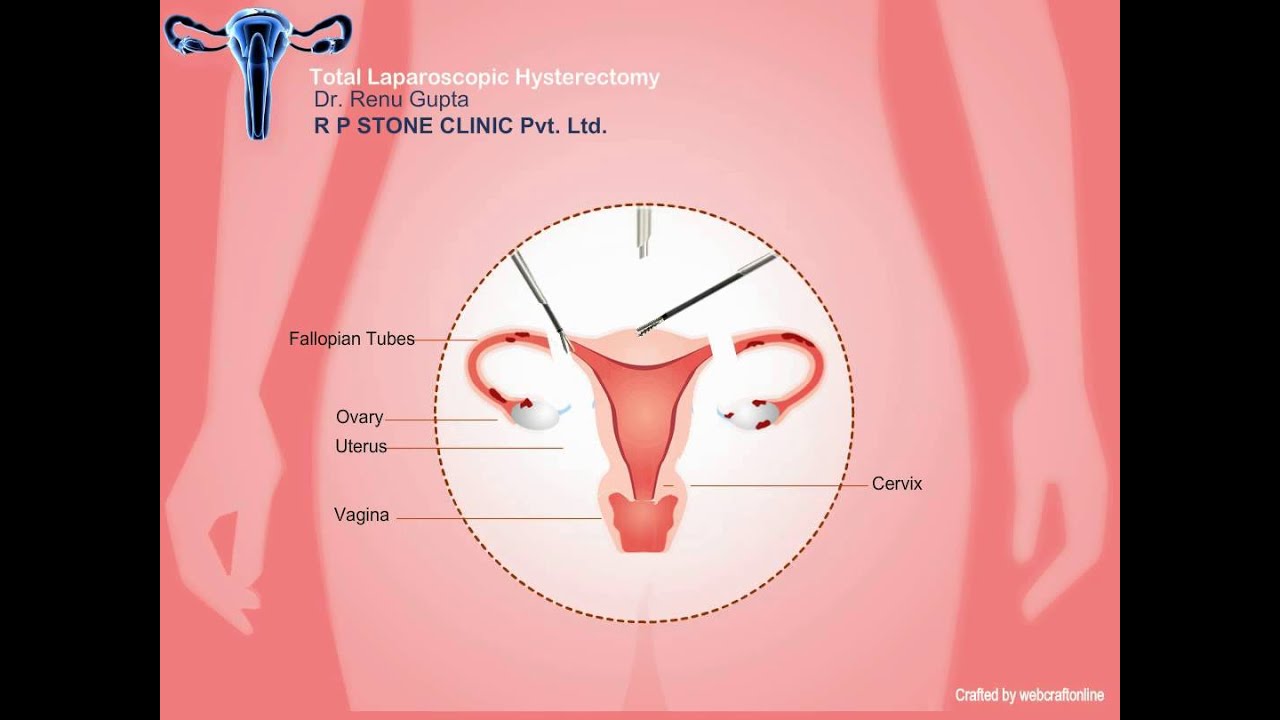
Laparoscopic oophorectomy is the surgical removal of an ovary through keyhole incisions. The removal of an ovary together with the fallopian tube is called salpingo-oophorectomy.
When both ovaries and both fallopian tubes are removed, the term bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy (BSO) is used.
When it is necessary to remove the ovary?
Oophorectomy is usually performed because of diseases such as ovarian cysts or endometriosis.
Normal non diseased ovaries are sometimes also removed as a prophylactic procedure to prevent ovarian cancer later in life. This is particularly appropriate in women with a family history of ovarian cancer and/or with genetic polymorphisms such as BRCA1/BRCA2 (A "cancer gene").
What does the operation involve?
Removal of the ovary and its associated fallopian tube requires the ovary to be dissected free of surrounding structures. The ovarian artery is sealed and cut, and the remainder of the attachments are then divided. The ovary is then usually removed from the abdomen through one of the laparoscopic (keyhole) ports.
What is recovery after surgery like?
The operation is usually performed as a day-case; the patient will go home on the same day. Recovery from any surgery varies considerably between individuals. There may be some bruising of the abdominal wall which can take about a week to settle and most women get some aching and mild discomfort for 48 hours; on average women would take about 3-4 days off work and delay driving for 48-72 hours.






















SORT BY-
Mga Nangungunang Komento
-
Pinakabagong komento